
In today's highly interconnected smart home era, we rely on an increasing number of devices. However, you've likely found that your VPN app only protects your phone and computer. Countless Internet of Things (IoT) devices—like smart TVs, gaming consoles (PS5, Xbox), smart speakers, webcams, and even smart refrigerators—are often left exposed on unencrypted networks. Moreover, the process of reinstalling, logging in, and managing VPN clients every time you buy a new device is simply tedious.
This guide is designed to help you navigate the complex 2026 router market. We will detail the most recommended VPN router models, categorizing them into three main types based on acquisition and configuration complexity. Finally, we will provide a detailed hardware buying guide and step-by-step setup instructions, ensuring you can easily achieve whole-home encryption.
VPN Routers: Concept and Core Value
As smart devices become ubiquitous, a single-device VPN client can no longer secure the entire home network. Configuring a VPN directly on the router is the ultimate "set-it-and-forget-it" solution for network protection.
1. What is a VPN Router?
A VPN router is a specialized device that can establish and maintain a direct VPN connection. This is achieved either through pre-installed VPN client firmware (like the ExpressVPN Aircove) or by flashing it with third-party open-source firmware (such as DD-WRT or OpenWrt).
-
Core Principle: Once the router connects to the VPN, every device linked to its network automatically receives encrypted protection, regardless of its operating system, type, or native VPN app support.
-
Core Benefit: VPN routers deliver whole-home device protection, fundamentally resolving network security and geo-restriction challenges.
2. Why Use a VPN Router? (Gaming, Smart TVs, Unlimited Devices)

A VPN router elevates network encryption to the very entry point of your home network, offering unique benefits traditional VPN applications cannot match:
|
Advantage |
Description |
|
Pervasive Protection |
A single configuration protects every device in the house, including IoT gadgets and guest devices. |
|
Total Compatibility |
Seamless integration with all devices. This is the definitive fix for streaming players (Apple TV, Roku) and gaming consoles that lack native VPN support. |
|
Always-On Security |
The router acts as the central hub, providing continuous encryption. This eliminates the risk of data leaks if users forget to activate the VPN or an app crashes. |
|
Simplified Experience |
Drastically improves user experience. Family and guests gain automatic security simply by connecting to the Wi-Fi. |
Best VPN Routers of 2026: Pre-flashed and Ready-to-Go
This section organizes routers into three primary categories to meet diverse user needs: convenience (VPN-Ready), immediate use (Pre-configured), and maximum control (DIY Flashing).
1. VPN-Ready Routers
VPN-Ready routers provide a VPN solution out of the box, requiring no complex firmware flashing. They feature built-in VPN client functionality in their factory firmware, offering an optimal blend of performance and simple setup. We sub-divide them based on protocol optimization:
A. WireGuard Optimized Routers (Recommended for NordVPN/Surfshark/Proton VPN)
If you plan to use high-performance services like NordVPN, Surfshark, or Proton VPN, native WireGuard support is essential, as these services perform best on WireGuard or its variants.

-
Recommended Model: RT-AX86U Pro, RT-AX82U, ROG Rapture GT-AX11000
-
Best Use Case: Multi-device households, high-performance gaming
- Key Feature: Exceptional Throughput: Supports policy-based routing for split tunneling. Capable of speeds up to 1 Gbps. Powerful processors ensure top-tier WireGuard performance. Merlin firmware adds a professional-grade Kill Switch.

-
Recommended Model: AX3000, BE19000, Archer GE800
-
Best Use Case: Simple, budget-friendly VPN entry point
-
Key Feature: Affordable Wi-Fi 6/7: Competitively priced models with native WireGuard client/server support via official firmware. Simple web setup and keep-alive features, perfect for beginners.

-
Recommended Model: Flint 2 (GL-MT6000), Beryl AX (GL-AX1800), Brume 2 (MT2500A)
-
Best Use Case: Frequent travel, high portability needs
-
Key Feature: Compact Security: Highly portable routers pre-installed with user-friendly OpenWrt. Simple configuration import. WireGuard speeds easily surpass 500 Mbps. Built-in AdGuard Home offers network-wide ad blocking.

-
Recommended Model: RT6600ax
-
Best Use Case: Advanced network management, professional-level control.
-
Key Feature: Pro-Grade Management: Features unique SRM firmware with robust traffic control. Supports VPN Plus and allows the creation of up to 5 separate Wi-Fi networks.
B. OpenVPN Native Support Routers
These routers natively support the OpenVPN protocol, offering compatibility with nearly all VPN services without flashing. While they can also run WireGuard (often through firmware updates or plugin installs), their key strength is reliable OpenVPN support.

-
Recommended Model: RT-AX88U Pro, RT-AX58U, GT-AX11000
-
Best Use Case: Gaming, large homes, universal compatibility
-
Key Feature: High OpenVPN Speed: Achieves OpenVPN throughput of 200–400 Mbps thanks to powerful hardware acceleration. Supports policy-based routing to exempt local traffic from the VPN tunnel.

-
Recommended Model: Flint 2 (GL-MT6000), Slate AX (GL-AXT1800)
-
Best Use Case: Travel, small offices
-
Key Feature: Portable and Secure: Delivers OpenVPN speeds over 300 Mbps. Compact and portable. The native OpenWrt system includes AdGuard Home, providing essential travel privacy protection.

-
Recommended Model: WRT3200 ACM, MX4200 (Velop)
-
Best Use Case: Customizable Mesh, secure remote access
-
Key Feature: Mesh and Customization: OpenVPN throughput up to 300 Mbps. Some models include built-in OpenVPN server support in the standard firmware, making secure remote access to the home network simple.
C: Top VPN-Ready Router Brands Analysis
Asus: Performance and Usability
-
Core Strengths: Asus is the market leader with an extensive model range covering all price points. Its powerful processors efficiently handle VPN encryption, providing a stable, high-performance experience. The native AsusWRT firmware supports multiple protocols, including WireGuard and OpenVPN, with setup typically taking less than 20 minutes.
-
Firmware Recommendation: The stock firmware has fewer features; we strongly recommend upgrading to the (free) Asus Merlin firmware to unlock advanced features (like a Kill Switch) and higher performance.
-
Important Note: Router model numbers are not the sole indicator of speed. Support for AES-NI acceleration on the specific processor is the crucial factor determining VPN encryption speed.
-
Target Audience: Home users and gamers seeking high performance, stability, and multi-protocol support.
TP-Link: Budget-Friendly WireGuard
-
Core Strengths: Many models (such as the Archer AX55) natively support WireGuard via the official firmware, requiring no flashing. TP-Link offers excellent value by combining WireGuard's light, fast protocol with affordable Wi-Fi 6 hardware.
-
Target Audience: VPN router beginners and users with a limited budget.
GL.iNet: Portability and Versatility
-
Core Strengths: These routers come pre-installed with WireGuard and OpenVPN support and are simple to configure. The Flint/Beryl Series is compact, making them ideal for travel or home office use. They feature integrated AdGuard Home for network-level ad blocking.
-
Target Audience: Frequent travelers and users who prioritize portability and enhanced privacy features.
Linksys: OpenVPN and Mesh Networking
-
Core Strengths: Certain models (like the WRT3200ACM) include built-in OpenVPN server support in their standard firmware, simplifying secure remote access. They also support Mesh networking, which is excellent for covering large homes.
-
Target Audience: Users requiring Mesh network coverage and OpenVPN server functionality.
2. Pre-configured VPN Routers
Pre-configured VPN routers are the ultimate shortcut for users demanding instant security and a zero-configuration experience.
|
Model |
Key Point |
Recommendation Reason |
|
Zero-config, pre-flashed custom ExpressVPN firmware, intuitive device grouping/split tunneling. |
Ultimate Ease of Use. True plug-and-play, security verified by ExpressVPN. The Go version is perfect for travelers. |
|
|
High-performance Wi-Fi 6 hardware, professionally optimized OpenWrt/NordLynx firmware. |
High-Speed Customized Option. Professionally configured by the third-party company FlashRouters. Deeply optimized for the WireGuard protocol, it offers top-tier VPN encryption speed paired with dedicated customer support. |
ExpressVPN Aircove Router>>
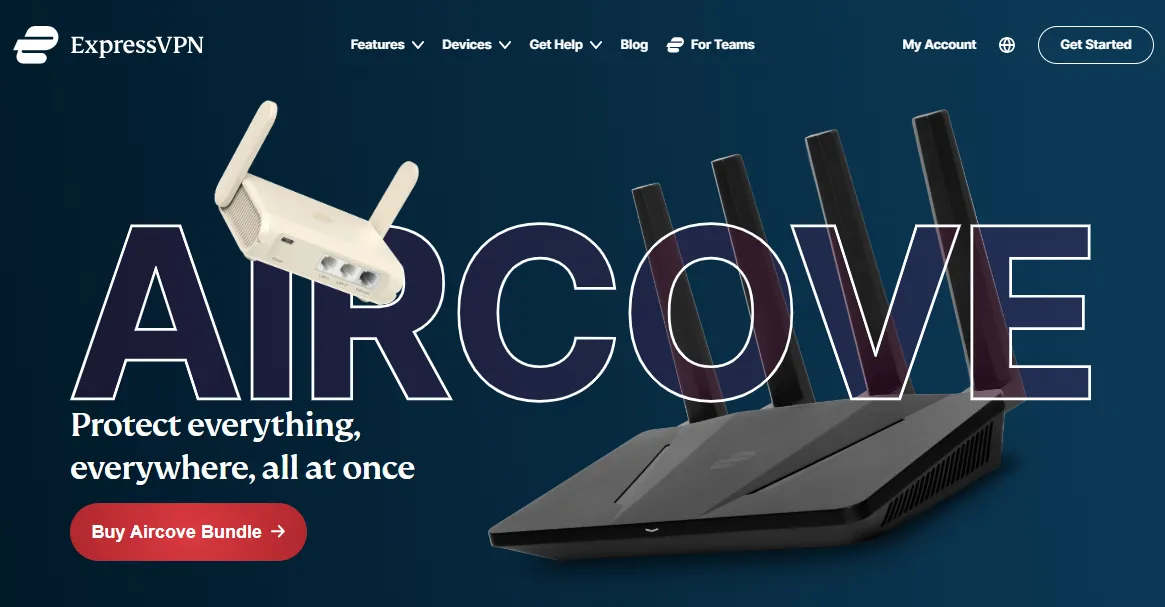
ExpressVPN’s Aircove series is designed for maximum simplicity, entirely removing the complexity of flashing and manual configuration. Users simply plug it in and activate their subscription; all connected devices are instantly protected.
-
Hardware Specifications: Wi-Fi 6, speeds up to 1,200 Mbps. Coverage approximately 1,600 sq ft.
-
Key Feature - Device Groups: The standout management feature allows users to organize devices into up to five groups (e.g., Family, Streaming, No VPN group). Users can then assign different VPN servers or connection settings to each group.
-
Subscription Benefit: The router itself only counts as one of the simultaneous connection slots in an ExpressVPN subscription.
-
Portable Version - Aircove Go: Features a compact design, USB-C power support, and Wi-Fi link functionality, allowing it to connect to an existing network without an Ethernet cable. It’s the ideal choice for business travel and digital nomads, offering a stable 600 Mbps speed (on the 2.4GHz band).
FlashRouters>>
FlashRouters is a VPN router vendor specializing in highly customized services and expert support. They offer pre-flashing services and lifetime technical support, allowing users to harness the power of open-source firmware without the inherent risk of flashing.
-
Core Value: Pre-installing and configuring powerful free and open-source firmware, such as DD-WRT, Tomato, and OpenWrt.
-
Target Audience: Ideal for advanced users who need the robust features and flexibility of open-source firmware but want to avoid the flashing risk.
-
Compatibility: Customers can specify the pre-installed firmware version, guaranteeing compatibility with major VPN providers (NordVPN, Surfshark, etc.).
-
Service Advantage: Users can select router models on their website already configured for a specific VPN service, streamlining the complex setup and debugging process.
3. DIY Firmware Platforms
These routers require users to manually flash third-party open-source firmware, granting ultimate control and powerful customization features. Due to the inherent risks of flashing, this option is recommended only for users with adequate technical knowledge.
Asuswrt-Merlin: Enhanced Asus Native Firmware (AsusWRT)
-
Key Advantages: Excellent stability, user-friendly interface, built-in VPN Kill Switch, flexible Policy Routing.
-
Best Suited For: Owners of compatible Asus routers who want stability and advanced features.
OpenWRT: Ultimate Open-Source Customization Platform
-
Key Advantages: Broadest device support, active community, extensive package management (e.g., AdGuard Home), total control.
-
Best Suited For: Advanced users and technicians seeking maximum control and specialized network functions.
DD-WRT: Veteran Third-Party Firmware
-
Key Advantages: Wide compatibility, supports many older router models, decent Quality of Service (QoS).
-
Best Suited For: Traditional users looking to extend the life of legacy equipment with basic VPN needs.
Tomato/AdvancedTomato: Feature-Balanced Alternative
-
Key Advantages: User-friendly GUI, strong policy-based routing, supports limited multi-VPN connections.
-
Best Suited For: Users prioritizing an intuitive interface and balanced feature set over deep customization.
pfSense: Professional-Grade Firewall OS (FreeBSD)

-
Key Advantages: Extreme performance and security, high-speed VPN handling.
-
Best Suited For: Power users or small businesses requiring professional-grade speed and firewall capabilities (requires dedicated hardware).
Buying Guide: How to Choose the Best VPN Router?
When selecting a VPN router, the core consideration is its capacity to handle encryption tasks, which is primarily determined by its hardware specifications.
1. Hardware Specifications (The Key to Speed)
Processor (CPU): Multi-core (Quad-core or higher), high frequency (1.5GHz+)
-
Importance: ⭐⭐⭐
-
Explanation: VPN encryption/decryption is CPU-intensive. A stronger processor means faster VPN connection speed. Crucially, support for hardware encryption acceleration (like AES-NI) boosts OpenVPN speed.
Memory (RAM): At least 512MB (1GB+ recommended)
-
Importance: ⭐⭐
-
Explanation: Adequate memory ensures the router runs stably and can manage a high volume of connection requests, especially with complex protocols like OpenVPN.
Wi-Fi Standard: Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) or Wi-Fi 7
-
Importance: ⭐⭐
-
Explanation: This is vital to ensure your local Wi-Fi speed does not bottleneck the VPN connection speed.
Port Speed: At least Gigabit Ethernet (1G) support. 2.5G or 10G ports are better.
-
Importance: ⭐
-
Explanation: Essential for Gigabit fiber users to prevent wired connections from becoming the speed bottleneck.
2. Firmware and VPN Protocol Support
-
Protocol Compatibility: WireGuard is currently the fastest and most efficient VPN protocol and is a must-have. OpenVPN offers the broadest compatibility and should also be supported.
-
Firmware Type:
-
Native Firmware (e.g., AsusWRT): Offers the highest stability and simplest setup.
- Third-Party Firmware (e.g., OpenWrt, DD-WRT): Provides powerful features but requires technical expertise.
-
3. Ease of Use and Brand Support
-
If you are a beginner, opt for a VPN-Ready or Pre-configured router, as they feature friendlier user interfaces.
-
Always choose brands (like ASUS, Synology, or GL.iNet) that provide regular firmware updates and reliable customer support to guarantee security and stability.
Essential VPN Router Setup Guide: Protocols and Firmware
The setup process for a VPN router varies depending on the router type and firmware.
1. Preparation (Prerequisites)
-
Select a VPN Provider: Ensure your chosen VPN provider (e.g., ExpressVPN, NordVPN, Surfshark) supports router configuration.
-
Obtain Necessary Files: Download the OpenVPN .ovpn configuration file or the WireGuard keys and configuration file from your VPN provider's website.
-
Ensure IP Conflict Avoidance: The IP address range of your VPN router must be different from your main modem/router (e.g., set the VPN router's IP to 192.168.2.1 instead of 192.168.1.1).
2. Three Main Setup Methods
Method 1: Using Native Firmware (GUI Setup)
This is the fastest method for VPN-Ready and pre-configured routers (e.g., Asus, ExpressVPN Aircove). The setup is done entirely through the router's graphical web interface.
-
Access Interface: Log in to your router's admin panel (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
-
Find VPN Client: Navigate to the "VPN Client" or "VPN Fusion" settings.
-
Import Config: Upload your .ovpn (OpenVPN) or .conf (WireGuard) configuration file from your VPN provider.
-
Enable & Route: Activate the connection and configure Policy Routing if you need to choose which devices use the VPN.
-
Verify: Connect a device and check your IP address on a tool like WhatIsMyIP.com.
Method 2: Flashing Third-Party Firmware (Advanced Operation)
This method is for users seeking maximum customization with open-source firmware like OpenWrt or DD-WRT. Risk Warning: Flashing can 'brick' your device. Proceed with caution.
-
Check Compatibility: Verify your router model is compatible with the desired firmware (DD-WRT/OpenWrt).
-
Download Firmware: Get the correct "Factory-to-Router" or "Web Upgrade" file for your specific model.
-
Flash Firmware: Use the router's admin interface to upload the new firmware. Do not interrupt the power or network connection during this step.
-
Configure VPN: After the router reboots, log into the new firmware and use the "Services" or "VPN" menu to configure the client settings.
Method 3: Manually Configuring the VPN Connection (Expert Users)
Required when the firmware lacks a GUI client. This gives expert users total control via the command line (SSH).
-
SSH Connect: Use PuTTY or Terminal to connect to the router (e.g., 192.168.1.1).
-
Install Client: Use the package manager (opkg for OpenWrt) to install the OpenVPN or WireGuard client software and dependencies.
-
Edit Config Files: Copy your VPN configuration content into the router's file system (e.g., /etc/openvpn/).
-
Setup Routing/Firewall: Configure network interfaces and firewall rules (e.g., using UCI or iptables) to direct traffic through the VPN interface.
-
Start Service: Start the VPN service and set it to auto-run on boot.
3. Advanced Setup: Split Tunneling
-
Concept: Split tunneling gives you control over which device or application traffic is encrypted via the VPN (e.g., streaming) and which traffic connects directly to the local network (e.g., banking apps, local printer).
-
Setup Method:
-
AsusWRT/Merlin: You can typically select a list of device IP addresses that should use the VPN directly within the VPN settings.
- OpenWrt/DD-WRT: This requires advanced configuration in the firewall or routing table, implemented by writing rules (iptables) to split traffic based on the source IP address.
-
VPN Router Troubleshooting: 5 Steps for Router Diagnosis and Fixes
Technical issues vary widely based on the router model, firmware, and VPN provider. Here are basic steps to quickly check and resolve common connection problems.
VPN Connection Failed?
If the connection is unstable or fails after configuration, follow these troubleshooting steps:
-
Double-Check VPN Credentials: Ensure the username and password used in the router firmware are precisely correct. This information is typically the same as your general VPN login.
-
Carefully Verify VPN Configuration: If you configured the VPN manually, re-read the setup guide. Even small mistakes (like an incorrect configuration file path or mismatched port number) can prevent a connection.
-
Try a Different VPN Server: The current server you are trying to reach might be temporarily down or congested. Download the configuration file for another server and test the connection again.
-
Check the Router's Local Internet Connection: Confirm that the router itself has a successful connection to the internet (i.e., the WAN port status is normal).
-
Seek Professional Support: If troubleshooting fails, the best practice is to first contact the router company's customer support team (as they are experts on the hardware and firmware). Second, contact the VPN provider's support team for assistance with the configuration file.
Conclusion
A VPN router is the single best investment for securing your entire home network. By integrating the VPN client at the router level, you not only provide seamless, always-on encrypted protection for all devices but also significantly simplify daily usage and management.
Whether you choose the VPN-Ready Asus RT-AX86U Pro for peak performance, the Pre-configured ExpressVPN Aircove for sheer convenience, or the DIY Platform GL.iNet Flint 2 for deep customization, selecting the right device is the crucial step toward protecting your home network privacy and ensuring unrestricted content access.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: Will a VPN router slow down my internet speed?
A: Yes. The encryption and decryption process is CPU-intensive, which inevitably leads to some speed reduction. However, the extent of the loss depends on two factors:
-
Router CPU Performance: The stronger the processor, the less significant the speed reduction.
-
VPN Protocol: The WireGuard protocol is significantly lighter and faster than the traditional OpenVPN protocol, making it the preferred choice.
Q2: How can I confirm my VPN connection is successful?
A: The simplest way to verify the VPN connection status is:
-
Connect a device to your VPN router's Wi-Fi.
-
Visit any "What is My IP Address" website (such as WhatIsMyIP.com).
-
If the displayed IP address matches the geographical location of the VPN server you selected, the connection is confirmed.
Q3: Why does my VPN connection frequently disconnect?
A: Frequent disconnection can be caused by several factors:
-
Insufficient Router Performance: Low-performance CPUs can become overloaded, particularly when using the OpenVPN protocol.
-
Firmware or Configuration Errors: Double-check that your configuration file is accurate, or try updating the router's firmware.
-
VPN Provider Issues: Try switching to a different VPN server node, or contact your VPN provider's support team for help.
-
MTU Setting Issues: Adjusting the MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) value in the advanced settings can sometimes improve stability.
Q4: Does a VPN router feature a Kill Switch?
A: The presence of a "Kill Switch" depends primarily on the firmware the router is running and the capabilities offered by your chosen VPN service.
Leading VPN providers often integrate this functionality into their custom firmware. It ensures that if the encrypted tunnel unexpectedly drops, the router will immediately block all network data transmission, effectively preventing any IP address or data leaks.
For pre-configured VPN routers like the ExpressVPN Aircove, this feature is typically enabled by default, requiring no user intervention. If you are manually configuring a VPN connection on a general-purpose router, you may need to locate and activate this crucial security option within the router's VPN client settings.
Q5: Does a VPN router offer Split Tunneling?
A: Support for Split Tunneling is entirely contingent on the router's current firmware. Advanced platforms such as DD-WRT, OpenWRT, or Asus Merlin usually allow this feature to be implemented.
Router-level Split Tunneling operates differently from an application client, typically focusing on device or IP address splitting. Users can designate which devices on the network (e.g., a smart TV) should pass through the VPN tunnel and which devices (e.g., a work laptop) should connect directly via the local network.
Some purpose-built VPN routers (like the ExpressVPN Aircove) provide a highly intuitive interface. This allows users to segment devices into multiple groups and assign different VPN server locations to each group, or simply bypass the VPN entirely, significantly enhancing configuration flexibility.